Moldeo por inyección de plástico vs Impresión 3D: ¿Cuál es el mejor método?
Pros y contras de los 2 métodos de moldeado más populares
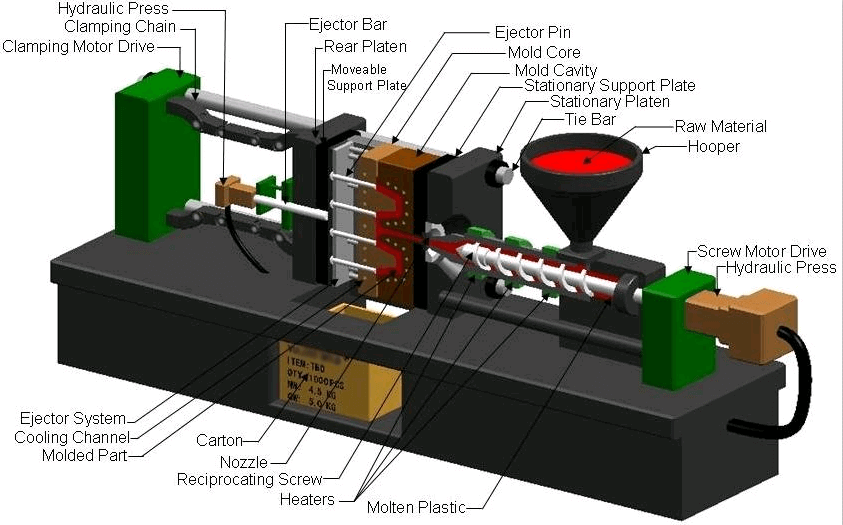
Moldeo por inyección de plástico en comparación con la impresión 3D
La Moldeo por inyección de plástico and 3D printing are two different production methods for the manufacture of parts for industry. Both of these methods allow professionals to obtain parts simply from three-dimensional designs. In this article, we will compare the two production modes to determine which types of applications correspond to them.
¿Cómo funcionan los dos métodos de producción?
Para comprender mejor los intereses, ventajas y desventajas de cada modo de producción, es importante conocer cómo funcionan. Y cómo estos modos se pueden integrar dentro de una unidad de producción.
Materiales necesarios para la impresión 3D
La fabricación mediante impresión 3D requiere una impresora 3D y consumibles. Existen diferentes tecnologías en el mercado en comparación con el Moldeo por inyección de plástico . Primero, FDM (modelado por deposición fundida) que utiliza bobinas de filamentos de plástico.
En segundo lugar, SLA (estereolitografía) que utiliza cartuchos de resina líquida. En ambos casos, la impresión permite obtener piezas mediante la impresión de sucesivas capas de material. Existe una gran cantidad de materiales que son más o menos sencillos de imprimir y tienen diferentes propiedades.
Moldeo por inyección de plástico: ¿cómo funciona?
As the name suggests, Plastic injection molding involves injecting molten material into a mold. Then, to let cool and harden the material in order to obtain the final piece. The injection molding method requires more elements than 3D printing.
An injection molding machine, also known as an injection press, will be required. This consists of a worm to convey the material in solid form. There is also a heating unit to melt the material.
Finally, the system has a high-pressure injector for filling the mold. The injection molding also requires a mold made previously. Most often it is made of aluminum, hardened steel or copper. Obviously, material is needed for the design of the final part.
The advantages of Moldeo por inyección de plástico / 3d printing production methods
These two technologies therefore differ in terms of the technique used to design the final parts and in terms of the material required for their use. 3D printing and Plastic injection molding also have different interests.
Benefits of 3D printing
Regarding 3D printing technology, we can consider that the investment cost in terms of material is relatively low. Indeed, there are a large number of machines on the market with very variable prices and accessible to any budget.

Additionally, layer-by-layer additive manufacturing technology makes it easy to detect during manufacturing whether the model has design errors. These can also be corrected quickly by reworking the 3D model.
Finally, 3D machines make it possible to design parts with very fine details very simply using support filament. Precision is one of the strengths of 3D printing.
Benefits of Plastic injection molding moldeo por inyección
The main advantage of the injection molding method lies in the ability to mass produce parts quickly and with high precision in design repeatability.
Then, the objects produced using injection molding have high strengths. In the sense that they are designed in one layer and in one go with the injection of all of the liquid material inside. of the mold.
Finally, the injection of material inside the mold makes it possible to guarantee exact compliance with the quantity of material necessary for the manufacture of the part. If the mold is well designed, there is no loss of material during the manufacturing process.
Disadvantages and limitations
Like all production methods used in industry, Moldeo por inyección de plástico and 3D printing also have certain limitations. It can be more or less mitigated or avoided depending on the method chosen.
The limits of 3D printing
3D printing is somewhat limited in terms of the build volume of the parts. Indeed, most of the machines available on the market have relatively small printing volumes. And they can be a brake for certain applications. There are however large volume machines (up to one cubic meter) but the initial investment will be higher.
3D printing has another limitation, linked in part to the printing volume of the machines. It is the capacity to produce parts in large series. It will still be possible to produce in small and medium series by opting for production 3D printers.
The weak points of Plastic injection molding
Regarding Moldeo por inyección de plástico, the main problem lies in the difficulty of obtaining complex geometries. Indeed, the creation of a mold requires to design an inversion of the final part. It limits and significantly complicates the possibilities in terms of design.

Correcting errors is also more complex. When a manufacturing error is found on injection molding, it will be necessary to completely recreate a new mold. This will be penalizing in terms of time and in terms of cost.
The cost which is also one of the limits of the injection. Indeed, the initial investment for this kind of production will be much higher than 3D printing. In addition, the design of new molds also represents a high cost to be taken into account when calculating the return on investment.
Conclusión
Si el propósito de la impresión 3D y el Moldeo por inyección de plástico is the same, namely the production of parts, it turns out that these two manufacturing methods each have their interests in particular applications.
De hecho, el moldeo por inyección será más interesante para la producción de piezas terminadas en grandes series. mientras que la impresión 3D, por el contrario, permitirá producir piezas con un diseño complejo en pequeñas series.
La inversión, menor para la impresión 3D, también será un factor a tener en cuenta en la toma de decisiones. ¿Qué método prefiere y para qué tipo de aplicación? No dude en compartir sus experiencias dejando un comentario debajo del artículo.



